- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
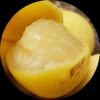
Cut Nut (Barringtonia Edulis)
Original price was: ₹3,330.00.₹2,360.00Current price is: ₹2,360.00.
Genus : Barringtonia
Grow your own Cut Nut Fruit Plant and savor the delectable taste of this tropical delicacy. The Cut Nut Fruit is known for its rich and buttery flavor, making it a favorite among fruit enthusiasts. With its smooth texture and nutritional benefits, the Cut Nut Fruit is a must-have for any garden. Plant the Cut Nut Fruit Plant in your garden and indulge in its unique and delightful taste.
Barringtonia edulis is a tropical fruit tree in the family Lecythidaceae that is native to the Pacific Islands, including Fiji, Samoa, and Tonga. It is commonly known as the Mango Pineapple or Fish Poison Tree.
The tree can grow up to 20 meters tall and has a dense, symmetrical crown. The leaves are large, glossy, and dark green, and the flowers are large, showy, and fragrant, with pink or white petals and long, protruding stamens. The fruit of the Barringtonia edulis plant is round or oval-shaped, and typically grows to around 10cm in diameter. It has a tough, woody outer shell, which must be removed to access the edible, juicy flesh inside. The fruit is usually eaten raw and has a sweet, tangy flavor that is often compared to a combination of mango and pineapple.
In addition to its culinary uses, the bark, leaves, and seeds of the Barringtonia edulis tree have long been used in traditional medicine for a variety of ailments, including skin conditions, fever, and pain relief. However, the tree is also known to contain toxic compounds that can be lethal to fish and other aquatic organisms, which has led to its use as a traditional fishing method in some areas.
The Barringtonia edulis plant is relatively easy to grow and maintain, and is adapted to tropical and subtropical climates. It prefers full sun and well-drained soils, and can be propagated from seeds or cuttings. Overall, the tree is valued for its delicious and unique fruit, as well as its cultural and ecological significance in the Pacific Islands.











Reviews
There are no reviews yet.