- Empty cart.
- Continue Shopping
- Home /
- Page
Planting and care
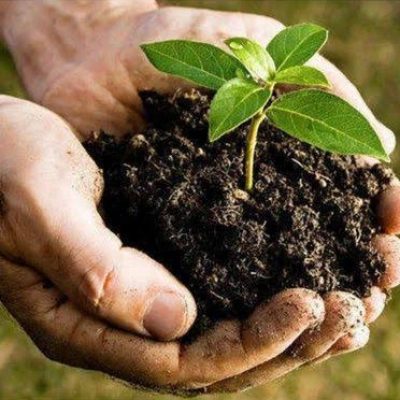
Planting and caring for plants involves several essential steps to ensure their growth and health


When you get the plant and remove its packet, you will see that the last grow bag has removed some soil and covered the bottom of the plant.
Open it up, what kind of soil do you intend to plant it in, fill it with soil, put it in a shed, water it twice a day, at this time do not give fertilizers for any reason. The first step is to adapt the plant to your nature.
Second stage is two weeks later cut the bottom of the plant’s grow bag and plant it where you plan to plant it. Still don’t fertilize.
About The Online Plants
Plants Bought Online Have To Survive Two Things

Online Plants Need to Survive one the Soil And Two the Atmosphere in your Place
Now the plant is matched to the ph level of your soil
After that, if your plant is struggling with your soil, you will see new leaves and buds coming or it will be stunted.
In both these conditions, you can give the required fertilizers to the plant
When applying fertilizers, apply them at a distance of one and a half feet from the base of the plant and apply organic fertilizers first
After that, how to fertilize
For that visit the planting & care page of this website. Or contact the executive in planting & care section
Fertilizer should be given if the plant is growing well
If it thrives well, you can use the same organic fertilizers that are used in your area
Fertilizer to be given if the plant is stunted
If the growth is stunted, find and use the fertilizers that the plant needs.
You can watch our YouTube video and learn about the plant



Here is a short description of the basic process:
Selection
Choose plants that are suitable for your climate, soil type, and available sunlight. Consider the purpose, size, and maintenance requirements of the plants you intend to grow.
Site Preparation
Prepare the planting area by removing weeds, rocks, and debris. Loosen the soil to improve drainage and root penetration. Add organic matter like compost to enrich the soil.
Planting
Dig a hole slightly larger than the plant's root ball. Gently remove the plant from its container and place it in the hole at the same depth it was previously growing. Backfill the hole with soil, firming it gently around the plant's roots
Watering
After planting, thoroughly water the plant to help settle the soil and eliminate air pockets. Water regularly, ensuring the soil remains moist but not waterlogged. Adjust watering frequency based on plant species and weather conditions.
Mulching
Apply a layer of organic mulch around the base of the plant, such as wood chips or straw. Mulch helps retain moisture, suppress weeds, and regulate soil temperature.
Fertilizing
Depending on the plant's nutritional needs, apply a balanced fertilizer during the growing season. Follow the instructions on the fertilizer packaging and avoid over-fertilization, which can harm the plant.
Pruning
Regularly inspect plants for dead, damaged, or diseased branches and remove them to promote healthy growth. Prune to maintain desired shape, control size, and encourage better flowering or fruiting
Support and Staking
Some plants, like tall flowers or vining vegetables, may require support or staking to prevent them from toppling over. Install stakes, trellises, or cages when necessary and secure the plants gently to them.
Maintenance
Regularly monitor plants' overall health and address any issues promptly. Provide additional care, such as deadheading spent flowers, thinning overcrowded growth, and dividing or repotting plants as needed.
Pest and Disease Control
Monitor plants for signs of pests or diseases. Identify the problem early and take appropriate measures, such as using organic insecticides, introducing beneficial insects, or practicing cultural controls like proper watering and spacing.
. Here are some common pests
and diseases that can affect Your plants:
Pests
Mealybugs
Mealybugs are small, soft-bodied insects that appear as white, cottony clusters on the plant. They feed on the sap of the plant, causing yellowing leaves and stunted growth. To control mealybugs, you can wipe them off the leaves with a cotton swab dipped in rubbing alcohol or use insecticidal soap.
Scale Insects
Scale insects are small, immobile pests that appear as tiny bumps on the leaves and stems. They feed on the plant sap, causing yellowing leaves and a sticky residue called honeydew. To control scale insects, you can scrape them off the plant using a soft brush or cloth, or use insecticidal soap.
Spider Mites
Spider mites are tiny pests that are difficult to see with the naked eye. They often create fine webbing on the plant and cause yellowing leaves and tiny brown spots. Regularly misting the leaves and using insecticidal soap can help control spider mite infestations.
Whiteflies
Whiteflies are tiny, winged insects that gather on the undersides of leaves, sucking sap and causing yellowing and wilting. Use insecticidal soap or horticultural oils to manage whitefly infestations.
Aphids
These small, soft-bodied insects can cluster on the new growth and undersides of leaves, causing stunted growth and deformation. Use insecticidal soap or neem oil to control aphids.
Fruit Spotting Bug (Amblypelta spp.)
These bugs feed on the fruit, causing blemishes and damage. They can be controlled through the use of insecticides and regular pruning to remove affected fruits. Anthracnose (Colletotrichum spp.): Anthracnose is a fungal disease that affects the fruit, causing dark, sunken lesions. To manage anthracnose, ensure proper air circulation, avoid overhead irrigation, and apply fungicides if necessary.
Caterpillars
Certain caterpillar species may feed on leaves, leading to holes and damage. Handpicking them off the plant or using organic insecticides can help manage caterpillar infestations.
Slugs and Snails
These creatures can eat holes in the leaves and damage the plant. Use physical barriers or organic slug repellents to protect the clematis from slugs and snails.
Thrips
Thrips are tiny, slender insects that feed on flowers, causing discoloration and deformation. Thrips can be challenging to control due to their size, but insecticidal soaps or neem oil can be used for management.
Fig Midge (Contarinia ficifolia)
Description: Small, gall-forming flies that lay eggs in young figs, causing malformation. Control: Prune affected fruits and use insecticides during the egg-laying period.
Fig Beetle (Cotinis mutabilis)
Description: Metallic green or bronze beetles that feed on ripe figs. Control: Harvest figs promptly, use traps, and apply insecticides if needed.
Coffee Berry Borer (Hypothenemus hampei):
Identification: Small beetle larvae that infest coffee cherries. - Damage: Larvae bore into coffee beans, reducing quality and yield. - Prevention and Treatment: Regular harvesting, proper sanitation, and applying insecticides.
Antestia Bug (Antestiopsis spp.)
Identification: Large, brown bugs that feed on coffee cherries. - Damage: Feeding causes discoloration and unpleasant flavors. - Prevention and Treatment: Proper harvesting and use of insecticides.
Termites
Termites can pose a threat to neem trees, especially to young plants. Protect the tree base with appropriate termite control measures
Pomegranate Butterfly
The larvae of certain butterflies may feed on pomegranate leaves. Handpicking or using Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) can be effective for control
Beetles
Certain beetles may feed on the leaves and flowers. consider using chemical controls such as insecticidal soap or fungicides. Always follow product instructions and use them judiciously.
Leaf-footed Bugs
Leaf-footed bugs feed on Sapota fruit, causing damage by puncturing the skin and feeding on the pulp. This can lead to fruit rot and premature dropping. pesticides as recommended by local agricultural authorities to control pest and disease outbreaks.
Sunflower Moth
The larvae of sunflower moth feed on developing sunflower seeds, causing damage to the seed head and reducing seed quality and yield. Regular monitoring of sunflower fields for early signs of pest or disease infestations is also critical for timely intervention and management.
Sunflower Beetle
Both adults and larvae of sunflower beetles can feed on sunflower leaves, causing skeletonization and defoliation of plants, particularly in the early stages of growth. To manage pests and diseases in sunflowers, it's essential to implement integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including cultural practices, biological control, and, if necessary, targeted pesticide applications.
Cutworms
Cutworm larvae may feed on sunflower stems at ground level, causing plants to wilt or collapse. They are most active at night and hide in the soil during the day To manage pests and diseases in sunflowers, it's essential to implement integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including cultural practices, biological control, and, if necessary, targeted pesticide applications.
Birds
Birds, especially finches, may feed on sunflower seeds, particularly as the seeds mature and dry on the plant. While birds can be beneficial for natural pest control, they can also reduce seed yield in commercial sunflower fields.Regular monitoring of sunflower fields for early signs of pest or disease infestations is also critical for timely intervention and management.
Fruit Flies
Fruit flies can infest ripe fruit, causing damage and promoting fungal growth. Fruit Flies Set up fruit fly traps around your plants using homemade or commercially available traps. These traps use bait to attract and trap fruit flies, reducing their population.
Leaf Miners
These pests lay eggs on leaves, and the larvae tunnel into the leaf tissue, leaving distinctive serpentine trails.If you notice any leaves with signs of leaf miner activity, promptly remove and destroy them. This helps prevent the spread of the pests to other parts of the plant.Planting flowers that attract these beneficial insects, such as marigolds or alyssum, can help keep leaf miner numbers in check.Neem oil, derived from the neem tree, can act as a repellent and disrupt the life cycle of leaf miners. Dilute neem oil according to the instructions on the product label and spray it onto affected plants.
Mites
Mites feed on plant cells, causing leaves to become stippled or discolored. They can also spin webs on the leaves and stems. Use insecticidal soap or horticultural oil to suffocate and kill mites. These products are less harmful to beneficial insects and can be effective against mites when applied properly.
Ginger Root Maggot (Conoderus sp.)
The ginger root maggot is a small fly whose larvae tunnel into ginger rhizomes, causing damage and reducing yield. Infested rhizomes may have tunnels and show signs of decay. . Follow all label instructions carefully and apply chemicals judiciously to minimize environmental impact and non-target effects.
Nematodes
Consider using beneficial nematodes (e.g., Steinernema feltiae) that prey on pest nematodes as a form of biological control. Apply them to the soil according to the manufacturer's instructions to suppress nematode populations
Flea Beetles
Flea beetles feed on spinach leaves, causing tiny holes and skeletonization of foliage. Use row covers to protect plants from flea beetles, apply diatomaceous earth as a natural deterrent, and use insecticidal sprays if infestations occur. Neem oil, derived from the neem tree, has insecticidal properties that can deter flea beetles and other pests. Dilute neem oil according to the manufacturer's instructions and spray it on the foliage of affected plants.
Cutworms
Cutworm larvae feed on spinach stems at ground level, causing wilting and damage to young plants. Protect seedlings with collars made from cardboard or plastic, handpick larvae in the evening, and apply biological controls like Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) if necessary.
Eucalyptus Longhorn Borer (Phoracantha spp.):
Longhorn borers are beetles whose larvae tunnel into the trunk and branches of eucalyptus trees, causing extensive damage and weakening the tree. Preventive measures include maintaining tree vigor through proper watering and fertilization, and promptly removing and destroying infested branches
Fruit Borers
Larvae of fruit borers may bore into the fruits, causing damage. Regularly inspect fruits for signs of entry holes or frass (insect excrement). Remove and destroy affected fruits to prevent further infestation.
Fruit Borers
Larvae of fruit borers may bore into the fruits, causing damage. Regularly inspect fruits for signs of entry holes or frass (insect excrement). Remove and destroy affected fruits to prevent further infestation.
Eucalyptus Psyllids (Glycaspis spp.
.Psyllids are small sap-sucking insects that can cause leaf distortion, wilting, and reduced growth. Control measures may include pruning affected branches, using insecticidal soap or neem oil, and introducing natural predators like ladybugs.
Eucalyptus Gall Wasp (Leptocybe invasa)
Gall wasps lay eggs in eucalyptus leaves and shoots, leading to the formation of galls that can deform leaves and stunt growth. Pruning and destroying affected branches, maintaining tree health, and applying insecticides during the wasp's active season can help manage infestations.
Citrus Leafminer
The larvae of this moth species tunnel through citrus leaves, leaving winding trails. While leafminers don't usually cause severe damage, heavy infestations can reduce fruit yields. Prune affected leaves and use sticky traps to monitor and control them.
Citrus Thrips
Thrips feed on young citrus fruits, causing scarring and distortion. Infested fruit may drop prematurely, reducing yields. Apply neem oil or insecticidal soap to control thrips populations.
Citrus Fruit Fly
: Fruit flies lay their eggs in citrus fruits, leading to larvae infestation inside the fruit. Infested fruit may prematurely drop from the tree or become unmarketable. Traps, baits, and sanitation measures can help control fruit fly populations.
Passion Vine Hopper (Scolypopa australis)
These sap-sucking insects can cause yellowing and distortion of leaves, as well as reduced fruit production.The Passion Vine Hopper (Scolypopa australis) is a pest native to Australia and New Zealand that primarily affects a variety of plants, including kiwifruit, passionfruit, and grapes Remove and destroy plant debris and weeds that may harbor eggs and nymphs. Horticultural oils can be effective in smothering eggs and nymphs.
Bean Leaf Beetles
These beetles feed on bean foliage, causing skeletonized leaves and reduced plant vigor. Handpick beetles from plants or use insecticidal sprays labeled for beetle control.
Mexican Bean Beetles
Similar in appearance to ladybugs but with distinct yellow markings, these beetles feed on bean foliage, resulting in defoliation and reduced yields. Handpick adults and larvae from plants, and use row covers to prevent infestation.
Stem Borer (Sesamia inferens)
Larvae bore into the stem, causing deadheart in young plants and chaffy panicles in older plants. - Management: - Use resistant varieties if available. - Rotate crops to break the pest lifecycle. - Apply neem-based pesticides or Bacillus thuringiensis (Bt) formulations. - Encourage natural predators like spiders and parasitoids
Shoot Fly (Atherigona spp.)
Caterpillars feed on leaves, creating large holes and defoliating plants. - Management: - Handpick and destroy caterpillars. - Apply biological control agents like NPV (Nucleopolyhedrovirus). - Use pheromone traps to monitor and control adult moths.
Armyworms (Spodoptera spp.)
Maggots feed on young shoots, causing deadheart. - Management: - Early sowing to avoid peak pest population. - Use seed treatment with insecticides. - Apply systemic insecticides during the early crop stages.
Citrus Red Mite:
Leaves and fruit may have a bronzed appearance. Severe infestations can cause leaf drop. - Management: Use miticides or horticultural oil. Ensure good air circulation and avoid water stress.
Borers
Insects that burrow into the wood, causing structural damage. - Control: Maintain tree health to resist infestations, and use systemic insecticides if necessary.
Deseases
Root Rot
Overwatering or poorly-draining soil can lead to root rot in plants. This fungal disease causes the roots to become mushy and discolored. To prevent root rot, ensure that the plant is potted in well-draining soil and allow the soil to dry out partially between watering sessions.
Leaf Yellowing
Excessive moisture or low light conditions can cause the lower leaves of the plant to turn yellow and eventually drop off. Adjusting the watering schedule and providing adequate light can help prevent this issue.
Viral Diseases
Plants can also be affected by viral diseases, which may cause mottling, stunting, or yellowing of the leaves. There are no cures for viral diseases, so prevention is crucial. Avoid planting near infected plants and practice good sanitation.
Leaf Browning
Exposure to direct sunlight or cold drafts can cause the tips and edges of the leaves to turn brown. Move the plant to a location with indirect light and away from cold drafts to prevent leaf browning.
Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew appears as a white, powdery coating on leaves, stems, and flowers. Improve air circulation, avoid overhead watering, and use fungicidal sprays containing sulfur or neem oil.
Leaf Spot
Leaf spot diseases cause dark spots on the foliage, leading to leaf drop. Remove affected leaves and ensure good air circulation around the plant to reduce humidity.
Botrytis Blight
Also known as gray mold, this disease can cause browning and decay of flowers and buds. Remove and discard affected plant parts, and avoid overhead watering to prevent the spread of botrytis blight.
Viral Diseases
Plants can also be affected by viral diseases, which may cause mottling, stunting, or yellowing of the leaves. There are no cures for viral diseases, so prevention is crucial. Avoid planting near infected plants and practice good sanitation.
Anthracnose (Colletotrichum spp.)
Anthracnose is a fungal disease that affects the fruit, causing dark, sunken lesions. To manage anthracnose, ensure proper air circulation, avoid overhead irrigation, and apply fungicides if necessary.
Rust
Rust is a fungal disease characterized by orange, rust-colored pustules on the undersides of leaves. It can lead to defoliation and reduced vigor in the plant.
Downy Mildew
This fungal disease causes yellow patches on the upper surface of leaves and a fuzzy, white growth on the undersides. Ensure good air circulation and avoid overhead watering to prevent downy mildew.
Fig Rust (Cerotelium fici)
Description: Fungal disease causing yellow spots on leaves, often leading to premature leaf drop. Control: Apply fungicides and practice good sanitation by removing affected leaves.
Root-Knot Nematodes
Description: Microscopic worms that infest the roots, causing root galls and reducing plant vigor. Control: Use resistant fig varieties, rotate crops, and apply nematode control measures.
Fig Mosaic Virus:
Description: Viral disease causing mosaic patterns on leaves and reduced fruit quality. Control: There is no cure for viral infections; focus on prevention, including controlling insect vectors.
Coffee Leaf Rust (Hemileia vastatrix)
Identification: Orange, powdery spots on leaves. - Damage: Defoliation, reduced photosynthesis. - Prevention and Treatment: Resistant plant varieties, fungicides
Coffee Berry Disease (Colletotrichum kahawae)
Identification: Dark lesions on coffee cherries. - Damage: Rotting of cherries. - Prevention and Treatment: Proper pruning, fungicides.
Wilt Diseases (Fusarium spp.)
Identification: Wilting, yellowing, and death of branches. - Damage: Reduced vigor and yield. - Prevention and Treatment: Resistant varieties, proper soil drainage.
Bacterial Blight (Pseudomonas syringae)
Identification: Water-soaked lesions on leaves. - Damage: Defoliation and reduced yield. - Prevention and Treatment: Copper-based fungicides, proper sanitation.
Bacterial Leaf Spot
This disease causes dark, water-soaked spots on leaves. Remove and destroy affected plant parts, and avoid overhead watering to reduce the spread of bacteria.
Crown Gall
Crown gall is a bacterial disease that causes abnormal growths on stems and roots. Infected plants may need to be removed to prevent the spread of the bacteria
Fruit Cracking
Cracking of pomegranate fruits can occur, especially in periods of uneven watering. Maintaining consistent soil moisture can help prevent fruit cracking.
Fungal Leaf Blight
Fungal leaf blight can lead to the development of brown spots on the leaves. Proper sanitation and avoiding overhead watering can help prevent this disease.
Blossom Blight
Blossom blight is a fungal disease that affects Sapota flowers, causing them to turn brown, wither, and drop prematurely. This can reduce fruit set and yield.fungicides as recommended by local agricultural authorities to control pest and disease outbreaks.
Botrytis Head Rot
Botrytis head rot is a fungal disease that affects sunflower flower heads, causing grayish-brown mold growth and decay. It is often associated with humid conditions and can lead to significant losses in seed yield and quality. To manage pests and diseases in sunflowers, it's essential to implement integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including cultural practices, biological control, and, if necessary, targeted pesticide applications.
Verticillium Wilt
Verticillium wilt is a soilborne fungal disease that causes wilting, yellowing, and necrosis of sunflower leaves. Infected plants may exhibit stunted growth, reduced vigor, and eventual death. To manage pests and diseases in sunflowers, it's essential to implement integrated pest management (IPM) strategies, including cultural practices, biological control, and, if necessary, targeted pesticide applications.
Gray Mold (Botrytis)
Gray mold is a fungal disease that affects flowers, causing them to become mushy and decay. It thrives in cool, humid conditions. As a last resort, consider applying fungicides labeled for controlling gray mold. Follow the instructions carefully, and apply fungicides preventatively or at the first signs of disease. Organic options like copper-based fungicides or biofungicides may be preferred for use in organic gardening.
Fusarium Wilt (Fusarium oxysporum)
Fusarium wilt is a fungal disease that affects the roots and stems of ginger plants. It causes wilting, yellowing, and stunting of growth. Infected plants may eventually collapse and die. Use biological control agents such as beneficial microbes or antagonistic fungi that suppress Fusarium wilt. These can be applied to the soil or used as seed treatments.
Rhizome Rot
Rhizome rot is a fungal disease that affects ginger rhizomes, causing soft rot and decay. Infected rhizomes may appear water-soaked and develop a foul odor. High humidity and poor drainage can exacerbate the problem. Consider using preventive treatments such as biofungicides or beneficial microbes that can colonize the rhizosphere and suppress the growth of pathogenic fungi.
Eucalyptus Rust (Puccinia psidii)
Eucalyptus rust is a fungal disease that causes orange to yellow rust-like lesions on leaves, eventually leading to defoliation and reduced tree health. Cultural practices such as improving air circulation, avoiding overhead watering, and applying fungicides containing copper or mancozeb can help manage rust infections.
Eucalyptus Leaf Spot (Cercospora spp. and Mycosphaerella spp.)
Leaf spot diseases cause dark spots or lesions on eucalyptus leaves, leading to premature leaf drop and reduced tree vigor. Removing and destroying infected leaves, improving air circulation, and applying fungicides labeled for leaf spot control can help manage these diseases.
Eucalyptus Decline Syndrome
Eucalyptus decline syndrome is a complex disorder characterized by dieback, leaf discoloration, and overall tree decline. Management strategies include promoting tree vigor through proper watering, fertilization, and mulching, as well as monitoring and managing pests and diseases that contribute to decline.
Citrus Canker
This bacterial disease causes raised lesions on leaves, fruit, and stems, which eventually lead to defoliation and fruit drop. Infected plant parts should be removed and destroyed to prevent its spread. Copper-based fungicides can help manage citrus canker.
Citrus Black Spot
This fungal disease causes dark, sunken lesions on citrus fruit, reducing their market value. Regular pruning to improve air circulation and fungicidal sprays can help control black spot.
Citrus Greening (Huanglongbing)
This devastating bacterial disease affects the vascular system of citrus trees, causing stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and bitter, misshapen fruit. There is no cure for citrus greening, so affected trees should be removed and destroyed to prevent its spread.
Nematodes
Nematodes are microscopic worms that can feed on the roots of the plant, causing stunted growth, wilting, and yellowing of foliage Certain plants, such as marigolds (Tagetes spp.), produce compounds that are toxic to nematodes. Planting these biofumigant cover crops and incorporating them into the soil can help suppress nematode populations.
Bean Rust
This fungal disease appears as orange-brown rust-like pustules on leaves, reducing photosynthesis and weakening plants. Practice good garden sanitation, provide adequate air circulation, and apply fungicides as needed.
Blast (Magnaporthe grisea)
Leaf spots with gray centers and brown margins, lesions on stems and panicles, reduced grain filling. - Management: - Use resistant varieties. - Practice crop rotation and avoid continuous cropping of finger millet. - Apply fungicides like tricyclazole or carbendazim.
Ergot (Claviceps fusiformis)
Honeydew secretion from infected florets, followed by the development of dark, hard sclerotia. - Management: - Use clean seeds and practice crop rotation. - Remove and destroy infected plant parts. - Apply fungicides during flowering if necessary.
Greasy Spot:
Yellowish-brown, greasy-looking spots on leaves, leading to defoliation. - Management: Apply copper-based fungicides. Collect and destroy fallen leaves to reduce inoculum.
Phytophthora Root Rot:
Stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and root decay. Trees may decline and die if severely affected. - Management: Ensure good drainage and avoid waterlogging. Use fungicides like metalaxyl or mefenoxam.
Huanglongbing (HLB) or Citrus Greening:
Yellowing of leaf veins, misshapen fruit with a bitter taste, and tree decline. HLB is spread by the Asian citrus psyllid. - Management: There is no cure for HLB. Remove and destroy infected trees. Control psyllid populations and use HLB-resistant rootstocks if available
Sooty Mold
Black, sooty fungal growth on leaves and stems, often growing on honeydew excreted by pests like aphids and scale insects. - Control: Manage honeydew-producing pests, wash off mold with water, and improve air circulation.
It's important to regularly inspect your plant for any signs of pests or diseases. Early detection and prompt treatment can help prevent the issues from spreading and damaging the plant. If the problem persists or worsens, you may consider consulting a local horticulturist or Ivy Paradise Planting & Care Exicutive for further assistance.
Planting & caring of various important plants
Here is a general description of the plants we commonly grow. Apart from this, each specific type of plant has its own care and fertilization. WhatsApp our planting & care executive to know more about it
Care and fertilization of short plants that can be grown in pots and growbags
Planting of bud plants, grafted plants, layered plants, seedlings plants and their subsequent care are mentioned here.
Vegetables can be grown in all weathers except rainy season. Good variety of vegetable seedlings can be planted on the floor and in polythene bags, plant pots, agro bags etc. after germination in a sunny place.
Orchids are a diverse family of flowering plants known for their exquisite beauty and often intricate flowers
Anthuriums are tropical flowering plants admired for their vibrant, heart-shaped blooms and glossy, dark green leaves
Planting air plants (Tillandsia) and ferns can be a wonderful way to bring greenery and natural beauty into your home or garden. Here are some guidelines for planting and caring for air plants and ferns:
The coconut palm is native to the tropical regions of Asia, but it is now cultivated in many tropical and subtropical areas worldwide
Lotus and water lilies are both beautiful aquatic plants that are often associated with serenity, tranquility, and natural beauty
Method of Regulating Soil Ph Level
There are several methods to regulate soil pH:
How To Make Organic Fertilizer
How to make Compost & Manure
Compost and manure are two types of natural fertilizers that can help improve the health and fertility of soil in your garden or yard
How to make Bone Meal, Blood Meal & Fish Emulsion
Bone meal, blood meal, and fish emulsion are all organic fertilizers commonly used in gardening and farming.
How to make Seaweed / Kelp Fertilizer, Green Manure & Warm Casting
Seaweed or kelp fertilizer, green manure, and worm castings are all organic fertilizers commonly used in gardening and farming
Use organic pesticides too. Organic fertilizers, cow urine, calendula, organic fungicides, organic pesticides such as agrigo, tobacco tincture, mixture etc. can be used.
Chemicalc Fertilizer

Home
.Visit to know our various services

Shop
Visit to purchase various products

Planting & Care
Answers to your doubts about plants












